Key takeaways
- LLMs can save managers time on preparing schedules, memos, onboarding plans, and report summaries: but always fact-check, edit for tone, and scan for bias before sharing.
- Start small with low-risk tasks and keep personal data out of prompts.
- Prefer enterprise AI tools to align with Canadian privacy practices.
- This guide includes 14 copy-paste prompts built to help managers of shift-based workers.
Wondering how to use AI at work as a manager? Here’s a practical guide for shift-based teams, with manager-tested uses (scheduling, memos, onboarding) and privacy-safe habits.
Quick Start: How to Use AI at Work (for Managers)
- Pick one low-risk task (draft, summary, checklist)
- Write a precise prompt with constraints
- Keep personal data out; use enterprise accounts
- Review for accuracy, tone, and bias
- Pilot with one team; measure time saved
- Document what’s AI-assisted vs. manager-only
AI is changing the way managers work. From automating admin tasks to helping prepare better communications, large-language models (LLMs) can boost productivity and free up time for what matters most: your people.
As of 2025, 88% of organizations report using AI in at least one business function (up from 78% a year earlier), though many are still scaling responsibly (McKinsey).
As one of the first shift-based industries to embrace this technology, manufacturing is setting the pace, and other frontline sectors like hospitality and retail are beginning to follow.
Looking for a place to start with AI at work? This article offers practical tips and prompts to help shift-work managers safely and efficiently start integrating AI into their daily routines.
Quick Guide to AI Terms
Before we get into best practices, here’s a short guide to AI-related terms you’ll see in this article.
- AI (Artificial Intelligence): A technology that allows machines to mimic human thinking and perform tasks like writing, analyzing, or translating.
- LLM (Large Language Model): A type of AI trained to understand and generate human-like text based on the instructions you give it.
- Generative AI: AI that can create new content, like text, images, or code, rather than just analyze existing data.
- Prompt: The question or instruction you give to an AI tool (ex.: “Write a job posting for a barista”).
- AI Model: The engine behind the tool (or chatbot) that processes your prompt and generates a response.
- ChatGPT: A popular AI chatbot developed by OpenAI, used to generate text, answer questions, and assist with tasks.
- Claude: An AI chatbot created by Anthropic, known for its focus on safety, reliability, and longer responses.
- Gemini: Google’s AI assistant, designed to help with writing, research, and productivity tasks.
- Copilot: AI assistant built into Microsoft’s tools, designed to help with writing, analyzing data, and automating everyday work tasks.
Other terms that are not in this article, but worth knowing:
- Agent: An assistant built into a chatbot that can take actions or complete specific tasks automatically, based on detailed instructions.
- Training data: The information an AI model was trained on that shapes how it responds: books, websites, articles, etc.
- Bias in AI: When an AI system reflects stereotypes or unfair assumptions based on the data it was trained on.
- Hallucination in AI: When AI generates false or made-up information that sounds real but isn’t accurate.
Best Practices for Using AI at Work
Using AI at work isn’t about replacing managers or staff, it’s about supporting them. LLMs can save frontline supervisors hours each week by helping draft job descriptions, write internal messages, and prep checklists.
But like any workplace tool, AI needs to be used responsibly. We’ve put together some key best practices to help you use it safely, effectively, and in line with your organization’s values.
Start with Low‑Risk Tasks
Start with low-risk tasks such as document drafts, summaries, templates, or translations. Avoid using AI to decide on hiring, performance ratings, or discipline. Keep those tasks human-led. As you scale, a good practice is to document which tasks are AI-assisted vs. manager-only.
💡For high‑impact decisions, rely on human judgment and proper HR procedures and tools.
Keep Private and Sensitive Data Out of Prompts
Avoid personal data in prompts (anything that can identify a person). In Canada, treat health, financial, biometric and similar details as sensitive.
To protect employee privacy and company data:
Don’t enter employee personal information, like names, SSNs, addresses, performance notes or phone numbers
Don’t enter business critical and confidential information
Generalize the context, and manually add sensitive details afterward, offline
🇨🇦 Privacy in Canada: Follow your organization’s privacy policy and PIPEDA principles. Prefer enterprise plans (ChatGPT Enterprise, Microsoft 365 Copilot) where inputs/outputs aren’t used to train models by default and admin retention controls exist. Avoid personal accounts for work and never include identifiable employee data in prompts. (Sources: OPC/PIPEDA guidance, OpenAI Enterprise privacy, Microsoft Copilot Enterprise Data Protection.)
Verify and Edit Everything
AI can produce outdated, incomplete, or incorrect information. Treat the AI’s response as a draft, not a finished document.
- Fact-check key details against trusted sources
- Revise tone and language to match your workplace
💡 Think of AI as a helpful assistant rather than an expert.
Watch for Bias and Fairness Issues
AI models reflect patterns in the data they were trained on. Unfortunately, that data often includes stereotypes or outdated assumptions. Re-read drafts for inclusive language and potential disparate impact in hiring or discipline:
- Check for inclusive language when drafting job descriptions or feedback
- Look out for biased wording around gender, age, race, or ability
- Adjust the output to reflect your organization’s equity commitments
Use Enterprise‑Grade Tools
Many free AI tools collect your data and use it to train future models. While it’s not bad when you’re doing personal stuff like coming up with dinner ideas for tonight, it can quickly get you and your business into trouble.
- Avoid personal accounts for work
- Prefer enterprise plans (ChatGPT Enterprise/Team, Microsoft Copilot for Microsoft 365) where inputs/outputs aren’t used to train models by default and retention controls exist
- Turn off data sharing and training options whenever possible
Lead people, not prompts
AI won’t replace your judgment. Use it to clarify expectations, draft coaching notes, and prep feedback, then add context only you have.
Use coach-style prompts: ask first (“What do you think is the best next step?”), then guide with specifics the AI helped you draft. This keeps decisions human and the tone supportive. AI can suggest options but at the end of the day, you own your decisions.
14 AI Prompts for Managers (Shift-Work Friendly)
AI tools are most helpful when you give them the right instructions (prompts). Use this 5-part prompt framework, then copy any of the 14 examples: goal, inputs (facts), constraints (tone/length), output format (table, bullets), success criteria (what ‘good’ looks like).
Use these as first drafts, edit for tone, accuracy, and privacy.
Each prompt includes:
- Which task you can achieve and how the AI can help you
- A sample prompt you can copy, paste, and customize
1. Write a Job Posting
When to use it
Quickly draft clear, engaging job descriptions that attract the right candidates.
Try this prompt
“Write a friendly, professional job description for a part-time barista at our downtown café in Calgary. Highlight key qualities like reliability, strong customer service skills, and availability on weekends and evenings. Previous experience is an asset, but not mandatory. Mention benefits such as paid breaks and free meals. Keep the tone welcoming and concise (around 200 words). Visit our website for more information about our establishment [add link to: yourwebsite]”
What info to provide
To get the best result, include:
- Job title and employment type
- Key skills or qualities you’re looking for
- Shift expectations (full-time, part-time, evenings, weekends)
- Salary range (between X and Y, depending on experience)
- Perks and benefits
- Company culture
- A link to your website or social media for context
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a ‘good’ answer looks like)
2. Create a Shift Checklist
When to use it
Quickly generate a clear, step-by-step to-do list for any type of shift, whether it’s opening, closing, or inventory management.
Try this prompt
“Generate a detailed closing shift checklist for a restaurant kitchen. Include tasks like cleaning equipment, restocking supplies, checking that all appliances are turned off, logging waste, and prepping for the morning crew. Present the checklist as a numbered list, using simple and clear instructions.”
What to provide
To get the most accurate checklist, include:
- Type of shift
- Work area or department
- Common tasks that must be done (be precise if necessary)
- Any health, safety, or cleanliness requirements
- Any additional optional tasks
- Copy of a previous checklist, if you have one
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a ‘good’ answer looks like)
3. Draft Staff Communications
When to use it
Save time writing clear, respectful messages to your team. Use it to share a new internal policy, a changed procedure, or a company update.
Try this prompt
“Compose a concise message to notify the evening shift that tomorrow’s start time is delayed by one hour due to a delivery delay. Ask them to confirm receipt. Use a friendly and professional tone.”
What to provide
To help the AI generate the right message, include:
- What the message is about (schedule change, reminder, update)
- Who it’s for (specific team or shift)
- Key details (what’s changing, when, why)
- Whether you want staff to confirm receipt or take action
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a ‘good’ team communication looks like)
4. Plan a New Hire’s First Day
When to use it
Create a structured onboarding plan that helps new employees feel welcomed, supported, and set up for success from day one.
Try this prompt
“Outline a one-day onboarding schedule for a new clerk starting Monday in our convenience store. Include a store tour, cash register training, shadowing a senior colleague, and a review of safety procedures. Present the plan hour by hour, from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m., including work breaks, using clear and welcoming language.”
What to provide
To tailor the plan to your needs, include:
- New employee’s job title and department
- Start time and length of the shift(s)
- Activities or trainings to cover (safety, systems, team introductions)
- Whether the plan should be hour-by-hour or in time blocks
- If the plan is for one or multiple days
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a ‘good’ onboarding plan looks like)
5. Summarize Shift Reports
When to use it
Turn lengthy or messy shift notes into clear, actionable bullet points.
Try this prompt
“Here are our shift notes from last night: [paste notes or add photo/file]. Summarize the key points into a bullet-point list of action items. Highlight any equipment issues, inventory shortages, or customer complaints that need follow-up.”
What to provide
To get the most useful summary, include:
- The original shift notes
- Any specific focus areas (inventory, customer service)
- Whether you want the output as bullet points, categories, or action items
- Any deadline or follow-up expectations
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a ‘good’ summary looks like)
💡Hint: most LLMs can read photos and images. If your notes are handwritten, take a picture and upload it, they should be able to get the information.
6. Write Quick Praise or Feedback
When to use it
Recognize great work or address small issues with clarity and care.
Try these prompts
“Write a short thank-you note to our housekeeping team for handling a sudden influx of guests last night. Highlight their professionalism and teamwork. Use a warm and appreciative tone.”
OR
“Draft a message to an employee who was 15 minutes late to the morning shift. Remind them of our start-time policy. Ask if there’s anything we can do to help them be on time or if their availability has changed. Keep it respectful and supportive.”
What to provide
For meaningful and appropriate messages, include:
- Who the message is for (individual or team)
- The situation or behaviour you’re responding to
- Any policies or expectations to reference (if applicable)
- Whether the message should invite a reply or not
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a ‘good’ feedback looks like)
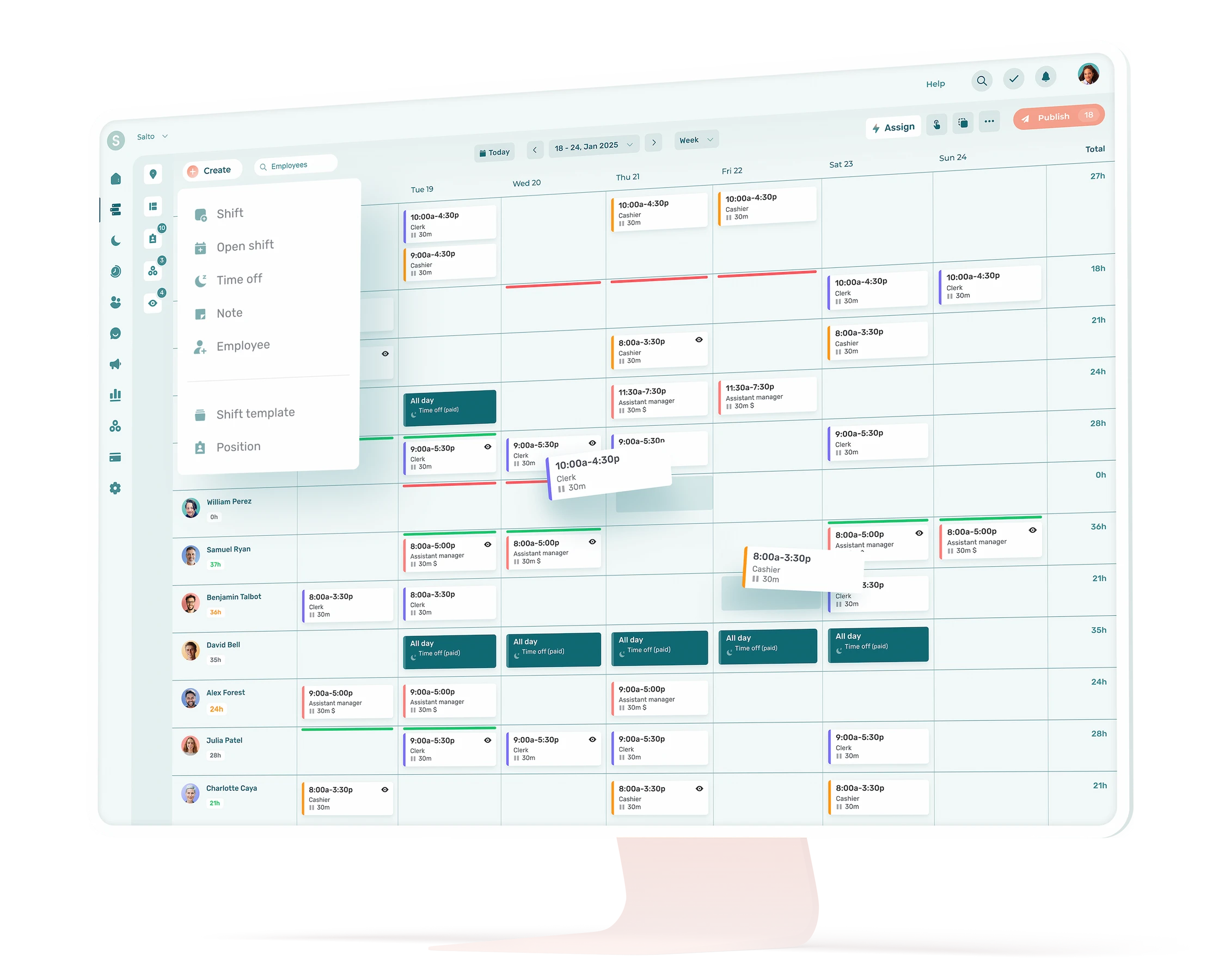
7. Generate a Weekly Schedule
When to use it
Build a fair and balanced weekly schedule and export it as a spreadsheet or Word document.
Try this prompt
“Create a weekly shift roster for a team of 6 café staff. We’re open Monday to Friday from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m., and Saturday and Sunday from 8 a.m. to 2 p.m. Make sure each employee gets at least one weekend day off and no more than 40 total hours. Present the schedule as a table with employee names, days, and shift times.”
What to provide
To generate a usable schedule, include:
- Number of employees, their first name and positions (avoid using details that can help identify individuals)
- Days and hours of operation
- Any scheduling rules (max hours, required rest days)
- Team availability or PTO requests
- Any role-specific needs (who can open/close, part-time vs. full-time)
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a ‘good’ schedule looks like)
💡Hint: LLMs can make downloadable spreadsheets and other documents, make sure to add the format you’d like in your prompt.
🚀 Take it one step further: when the next period comes, use the previous schedule and start from the same conversation to save time. Simply add the changed requirements.
📸 Want to go even faster? Upload a photo or file of your current schedule to Agendrix: AI will turn it into a complete secure digital version with employees, positions, and shifts. From there, you can use automatic scheduling to plan future schedules even faster.
8. Design a Quick Training Quiz
When to use it
Reinforce staff learning after rolling out new products, procedures, or policies. This could also be useful during employee onboarding.
Try this prompt
“We’ve just introduced three new sandwich recipes. Generate a five-question multiple-choice quiz to test our kitchen staff’s knowledge of ingredients and preparation steps. Provide the correct answers at the end. Here are the recipes [add recipes]”
What to provide
For an accurate and helpful quiz, include:
- A description of the topic or new procedure
- Specific points you want to test (steps, safety rules, ingredients)
- Number of questions
- Question format (multiple choice, true/false, open answer)
- Whether to include correct answers at the end
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a ‘good’ answer looks like)
9. Draft Policy Updates and Memos
When to use it
Communicate procedural changes or new guidelines clearly and consistently.
Try this prompt
“We have a new health and safety protocol for handling hot surfaces. Draft a one-page memo explaining why the change is needed, what the new procedure is, and how it benefits employees. Here are some notes regarding the protocol [details].”
What to provide
For accurate and appropriate memos, include:
- The reason for the policy or procedure change
- What the new policy involves (steps, requirements, deadlines)
- Who it applies to
- Any benefits or rationale to highlight
- Any important details
- Possible changes to tasks or operations
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (memo or policy example)
⚠️ Review contents: Always review AI-generated memos carefully. Add confidential details manually and ensure the content complies with your internal policies and legal obligations. Have your HSE or HR representative (if you have one) review the contents before sharing.
10. Summarize Meeting Notes into Action Items
When to use it
Turn rough or handwritten meeting notes into a clear, organized list of decisions and next steps.
Try this prompt
“Here are my notes from our weekly staff meeting: [paste notes]. Summarize the key decisions and action items in bullet-point form. Include who is responsible for each task and any relevant deadlines.”
What to provide
To get a clear summary, include:
- The full meeting notes (copied into the prompt or upload a photo)
- What type of meeting it was (weekly, staff check-in, opening)
- Whether to include responsible team members and deadlines
- Key themes or priorities to highlight (customer issues, staffing, upcoming events)
- Non-actionable items that should be excluded (general discussion, personal updates)
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (what a good action items list looks like)
11. Prepare Performance Feedback Drafts
When to use it
Draft thoughtful, balanced feedback for performance reviews, 1:1 meetings or coaching sessions.
Try this prompt
“Draft a short performance review summary for a sportsgoods clerk who consistently arrives on time, helps colleagues, but needs to improve their upselling skills. Include at least three specific examples, two strengths to praise, and one development goal with suggested training. Keep the tone professional and supportive.”
What to provide
To generate helpful feedback, include:
- The employee’s strengths and areas for improvement
- Specific examples of behaviours or contributions
- Areas of improvement, in any
- Any goals or expectations they’re working toward
- Whether the output is for a review, coaching note, etc.
- Notes from a previous feedback session (if available)
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (example of other performance feedback—keep anonymous)
💡Hint: Always personalize performance feedback and ensure it aligns with your workplace standards and policies.
12. Draft Standardized Operating Procedures (SOPs)
When to use it
Create clear, step-by-step documentation for routine tasks and ensure all team members follow the same process, no matter who’s on shift.
Try these prompts
For a restaurant:
“Write a standard operating procedure for safely handling food deliveries at a restaurant. Include steps such as checking delivery times, inspecting food quality and temperature, documenting invoices, rotating stock, and storing items appropriately. Format it as a numbered list and assign tasks per position.”
For a pharmacy:
“Create a standard operating procedure for receiving and storing new shelf medication deliveries. Include steps for checking inventory accuracy, inspecting packaging, updating stock records, and organizing products according to expiry date. Use clear, professional language, format as a numbered list, and assign tasks per position.”
For a retail store:
“Generate a step-by-step SOP for opening a hardware store each morning. Include tasks such as unlocking the store, turning on lights and music, bringing seasonal items outside, starting the POS system, inspecting displays, and restocking essential items. Present it as a clear, numbered list, with responsibilities per position.”
What to provide
To get a useful SOP, include:
- The type of task or process you want to document
- Your industry or work environment
- Any specific steps or compliance rules to include
- Who is responsible for what, when you can
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
- Success criteria (example of previous or other SOP)
13. Translate Team Messages
When to use it
If you’re working with a bilingual team, quickly translate team communications such as shift updates, reminders, or announcements.
Try this prompt
“Translate this shift announcement into French: “Reminder: Tomorrow’s team meeting starts at 3 p.m. sharp in the break room. We’ll discuss the new safety checklist and upcoming holiday schedules.” Provide both English and French versions in a clear format.”
What to provide
For an accurate translation, include:
- The original message (short and clearly written)
- The target language(s)
- Whether to include both the original and the translated version
- Any key terms to translate carefully (equipment names, procedures)
- Improvements or additional information to add to the original message, if any
- Constraints (context, format, tone)
⚠️ Review contents: always double check translations using a proper translation tool or ask an employee who is fluent in the target language to review it.
14. Design Quick Coaching Questions or Check‑Ins
When to use it
Guide meaningful one-on-one conversations with your team. Use coaching questions to support reflection, encourage accountability, and build trust.
Try this prompt
“Generate five open-ended questions I can ask a hotel receptionist about their recent performance. Questions should encourage them to share successes, challenges, and ideas for improvement without feeling judged.”
What to provide
To generate useful questions, include:
- The context (regular check-in, post-review, performance dip)
- Focus area (customer service, communication, time management)
- Industry and position
- Recent challenges the employee has, if any
- Recent successes to highlight, if any
- Notes from previous feedback sessions, if any (make sure to keep sensitive data out)
- Whether you want general questions or tied to specific goals/tasks
- Constraints (word count, format, tone, level of detail)
These prompts require no special software: any LLM can respond to them. For shift managers, they offer a practical way to save time, improve clarity, and support your team more efficiently.
Use AI Wisely, Lead Confidently
AI isn’t just for tech teams. It’s a time-saving, useful tool that can greatly benefit frontline managers. Whether you’re planning schedules, onboarding new staff, or drafting quick messages, the key is to use it wisely:
- Stick to low-risk tasks
- Review everything before sharing
- Protect employee privacy
- Stay transparent when it matters
By combining your leadership with the right AI prompts, you can spend less time on admin and more time supporting your team and managing your business.
How to use AI at work as a manager?
Start with one low-risk workflow (drafts, summaries, checklists). Give the AI tool clear inputs, constraints, and a desired format. Keep personal data out of prompts. Review outputs for accuracy, tone, and fairness before sharing, and document what’s AI-assisted vs. manager-only. A risk-based, incremental rollout aligns with leading governance guidance.
What is generative AI and how does it help shift work managers?
Generative AI creates new text, images, or code from your instructions. For managers, it speeds up first drafts (job posts, memos, schedules, SOPs, onboarding plans, etc.) so you can focus on coaching and decisions. Treat outputs as drafts that need human review for accuracy, inclusivity, and policy fit.
How can I use an LLM to write a job description or job posting?
Provide role, skills, shift expectations, pay range (if allowed), tone, and format. Ask for inclusive, plain language and a concise structure. Then edit for accuracy, compliance, and equity before publishing. Avoid adding identifiable personal information to prompts. Follow your privacy policy and Canadian obligations.
Can ChatGPT create daily or shift checklists?
Yes. Describe the shift type, tasks, and any safety or cleanliness rules. Request a numbered list and role-based responsibilities. Always review onsite to ensure steps match your operation and legal requirements, then adjust as needed.
Are there risks to using AI for HR documents like job descriptions or memos?
Yes. HR content affects hiring, fairness, and employee understanding. Use enterprise tools with admin controls, avoid personal data in prompts, and review drafts for bias and clarity before sharing. Ensure your use complies with Canadian privacy principles (e.g., meaningful consent and appropriate purpose).
How can AI help with employee performance feedback?
It can structure balanced notes (strengths, examples, goals), suggest phrasing, and reduce blank-page time. You still decide the message, ensure fairness, and tailor tone to your culture. Keep personal data out of prompts unless you’re on approved enterprise tools and follow internal policies.
How do I protect sensitive information when using AI?
Keep identifiable employee data out of prompts (names linked to issues, health details, contact info). Prefer enterprise plans where inputs/outputs aren’t used to train models by default and where retention/admin controls exist. Follow your privacy policy and PIPEDA obligations (meaningful consent, appropriate purposes).
Will using AI replace my role as a manager?
No. AI accelerates drafting and organization, but managers provide context, judgment, and people leadership. Most organizations are still piloting or scaling responsibly; human oversight remains essential for quality and risk management.
As a manager, you bring the coaching, decision-making, and people skills that keep your team engaged and supported.
Is it safe to use ChatGPT at work?
Use enterprise plans with admin controls and “no training by default” data handling. Keep personal data out of prompts and follow internal policies. Consumer accounts can have different retention and sharing rules. When in doubt, consult IT/legal and your privacy team.
What’s the best first workflow to automate?
Pick a low-risk, high-volume task: drafting memos, shift checklists, meeting/action-item summaries, or SOP outlines. Define inputs, constraints, and a review process. Pilot with one team, measure time saved, and expand gradually under your risk framework.
Can I include employee names in prompts?
Avoid it. In Canada, names tied to workplace details are personal information. Unless you have a clear legal basis and approved enterprise safeguards, keep prompts de-identified and add specifics after review. Follow your organization’s policy and PIPEDA principles.
What AI tools are OK for Canadian employers?
Choose enterprise-grade tools that commit to not using customer content to train models by default and offer admin/retention controls (ChatGPT Enterprise, Microsoft 365 Copilot/Azure OpenAI). Implement them under your privacy policy and governance program aligned to Canadian guidance. Consult IT/legal before rollout.